告別飢餓禁食!週期性模擬禁食飲食(PFMD)火了!減重、抗癌、延壽多管齊下!_風聞
时光派-时光派官方账号-聚集全球前沿、全面、专业抗衰资讯09-04 08:11

導言
作為與我們日常生活聯繫最緊密的抗衰手段之一,禁食因其減肥 [1]、延壽 [2-9]、改善健康狀況 [2-9]等功效一直備受抗衰愛好者們的青睞。
不過,都説是禁食了,自然免不了那麼每天十幾小時或是每週一兩天,甚至每月幾天的飢餓時光,對於有些朋友來説,這樣的時光不僅難以堅持,甚至可能存在營養不良等健康風險 [10-13]。
如果你也抱有這樣的疑慮,那定期模擬禁食飲食會是你的一個好選擇。沒聽過這個名字?沒關係,哈爾濱醫科大學的牛玉存教授團隊發表於Nutrition Reviews雜誌的一篇文章 [14]會幫助你全面瞭解它!


禁食延壽但傷身?
模擬禁食飲食:不捱餓的禁食來了!
根據禁食的持續時間以及頻率,我們一般可以將各種禁食干預手段分為兩大類:間歇性禁食和週期性禁食。
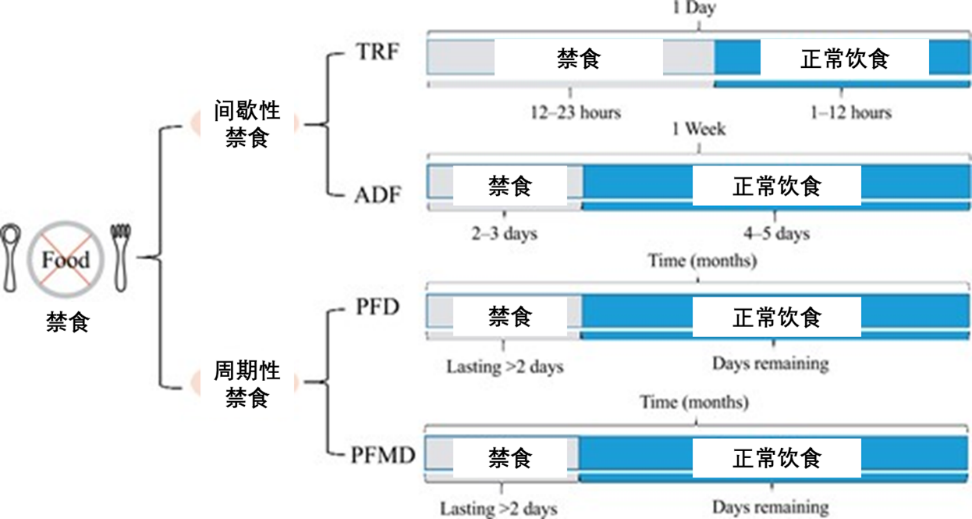
週期性禁食的禁食時間比較長,需要在大於2天的時間內持續維持禁食狀態,不過一般一個月甚至幾個月才會進行一輪。換句話説,你可能每個月都得要在那麼連續三四天裏堅持除了水以外粒米不進,這也就自然會帶來營養不良的潛在風險 [10-13]。
也正是為了解決這一問題,間歇性飲食應運而生。
相比之下,間歇性禁食的禁食時間往往持續較短,一般在幾小時到1到2天,且禁食週期也較短,每天或是每週進行一輪,像很多朋友可能都嘗試過的**16+8禁食法或是隔日禁食(即每週5+2禁食)**法,就都是間歇性禁食的一種 [10-13],他們的依從性和安全性也要更好一些。

圖注:圖片來源:https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/is-intermittent-fasting-safe-for-older-adults
這時肯定還有朋友叫嚷:這樣隔三差五不吃飯,還是好折磨哇,有沒有更好的方案呢?
以前沒有,但在**週期性模擬禁食飲食(Periodic Fasting-Mimicking Diet, PFMD)**誕生之後,可能就有了。
顧名思義,PFMD正是一種源自週期性禁食的新方法 [15]。與週期性禁食不同的是,在那持續數天的飢餓時光裏,我們並不需要完全辟穀啥都不吃,而是可以吃一些熱量並沒有那麼高的成分 (有關PFMD的具體如何實踐可參考本文的第三部分哦)。

圖注:PFMD的提出者、美國南加州大學Valter Longo教授,圖片來源:https://www.valterlongo.com/
在科學家們的辛苦耕耘之下,PFMD的動物和臨牀功效均已經得到了廣泛的研究,其不僅被證實對各種動物模型的健康和壽命有積極影響 [16-18],並且有益於人體健康,在治療各種疾病方面均表現出協同作用 [19-21]。
接下來就讓我們PFMD具體都在哪些方面發光發熱吧!

延壽減肥改善認知,多管齊下全面改善健康
No.1
延長壽命、改善健康狀態
之前的研究證實,禁食能夠激活AMPK通路介導抑制mTOR靶點 [22, 23],並且還可以降低血糖和甘油三酯水平[24]、改善體內胰島素抵抗 [25],最終達到延長壽命的效果。
與禁食類似,PFMD也被證實具備延長壽命的效果 [15, 26]。例如,雌性小鼠在每個月接受為期4天的PFMD後其壽命相關標誌物(如IGF-1)就能夠得到改善,其中位壽命延長了11% [15]。
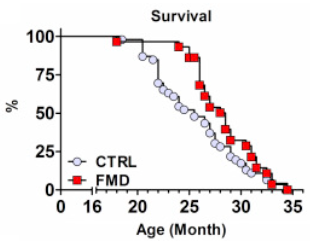
圖注:圖片來源:[15]
不過值得注意的是,高齡小鼠在接受PFMD後死亡率卻增加了,這表明對於一些過於年老體弱的羣體,禁食可能並非是一個好選擇 [15]。
在臨牀試驗中,PFMD同樣顯示出了顯著的益處 [27-29],其可以改善年齡相關疾病的生物標誌物或風險因素,如IGF-1、胰島素、葡萄糖、胰島素抵抗、糖化血紅蛋白、C反應蛋白、高血壓和高膽固醇等等 [27, 30]。
令人驚喜的是,哪怕是在PFMD干預完成3個月後,其對於受試者IGF-1、血壓等的影響仍然持續 [27]。牛玉存教授團隊指出,這表明PFMD有可能對參與者的健康狀況以及壽命產生持久的有益影響,是一種很有前途的衰老幹預手段 [14]。

圖注:圖片來源:https://www.bioagehealth.com/how-intermittent-fasting-can-help-to-fight-aging/
No.2
改善年齡相關疾病
在接受連續3天的PFMD後,帕金森小鼠成功避免了運動功能的減退,並改善黑質中多巴胺能神經元的損失,此外,腦源性神經營養因子的水平也得到了改善 [31]。相關研究則指出,這些改善作用有可能和其對腸道微生物羣組成的調節作用有關 [31]。
PFMD對我們的另外一個老熟人——老年痴呆同樣具有積極影響。實驗結果表明,每月連續5天的PFMD能夠減少老年痴呆小鼠海馬區Aβ蛋白沉積和tau蛋白過度磷酸化,並促進神經發生 [32]。
不過可惜的是,針對PFMD對帕金森和老年痴呆狀態改善的臨牀試驗目前還沒有取得足夠進展,僅有初步的臨牀觀察證明了其在老年痴呆患者中的安全性和可行性 [32]。
圖注:圖片來源:https://www.biospace.com/article/do-therapies-for-alzheimer-s-and-parkinson-s-that-clear-abnormal-brain-proteins-make-the-diseases-worse-/
No.3
減輕體重
小鼠實驗表明,PFMD可減輕體重並減少內臟脂肪 [15],且多次PFMD能夠避免恢復正常飲食後的體重反彈 [15]。除此之外,PFMD還被證實對肥胖具有預防作用 [33],這可能與其能夠上調幾個與脂肪酸氧化相關基因的表達、促進白色脂肪分解有關。
在臨牀試驗方面,也有研究證實每個月持續5天PFMD能夠促進參與者的體重減輕、整體脂肪和軀幹脂肪減少,以及代謝狀態改善 [27],這對肥胖的預防和治療都有顯著的有益作用。
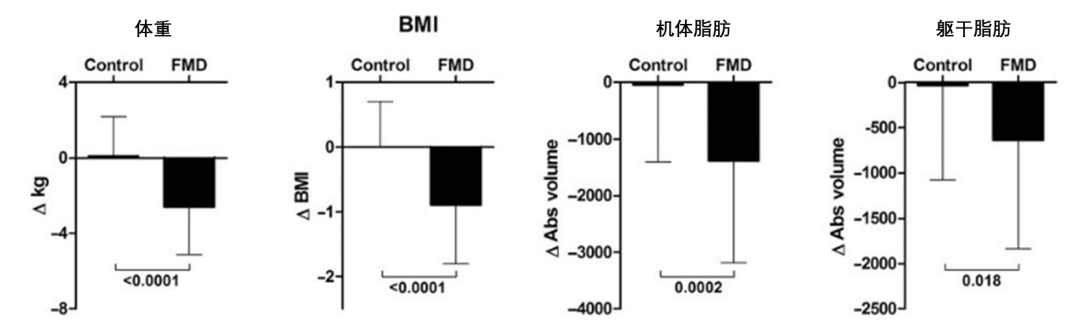
圖注:編譯自:[27]
No.4
改善糖尿病
科學家們發現,PFMD能夠有效降低血糖水平、並改善糖尿病患者的治療預後 [34],而糖尿病正是許多老年人的主要壽命威脅。
No.5
改善癌症
PFMD也被證實對小鼠具有顯著的抗癌作用,這可能是通過減少促癌因子和抑制 AKT-mTOR通路來實現的 [35]。

每月5天,多吃這幾樣,禁食收益就拿好
讀完上文,想必大家都已經知道了PFMD的好處,那我們到底應該怎樣操作實踐呢?
派派這裏為大家選取了一篇人體臨牀實驗研究 [27]中的設計為參考,在這項實驗中,參與者被要求每個月連續5天食用定製的PFMD飲食,並在完成後恢復正常飲食,直到大約25天后開始下一個週期。
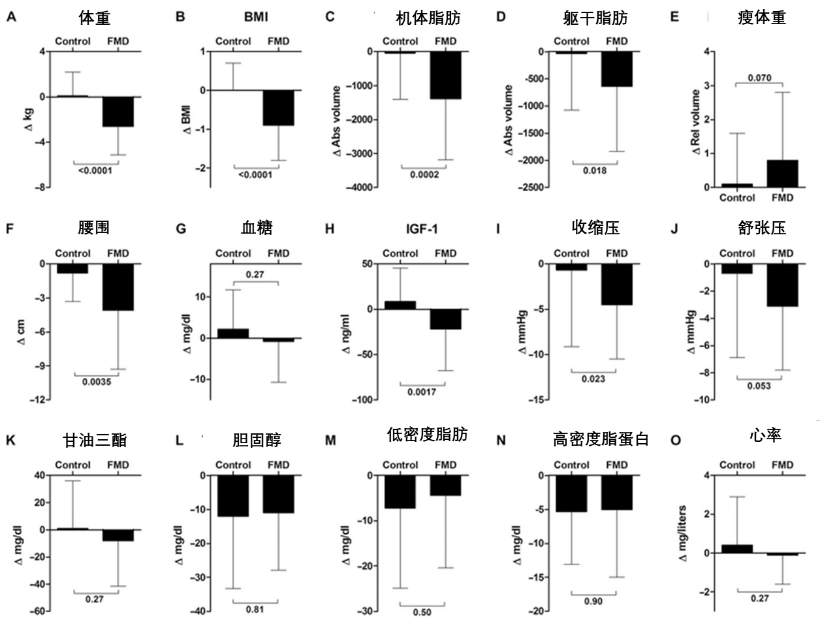
圖注:據該研究報道,PFMD在各個方面都對人體的健康狀態有所改善,圖片編譯自:[27]
在這5天的模擬禁食計劃中,**研究人員第一天為參與者提供約4600kJ(11%蛋白質、46%脂肪和43%碳水化合物)的食物,第2至5天則每天提供約3000kJ(9%蛋白質、44%脂肪和 47%碳水化合物)**的食物。
這些食物的種類也頗有講究,以蔬菜水果以及堅果為主,其中蔬菜被加工製作成了沙拉、燉菜或是湯以增加飽腹感,而脂肪則主要由橄欖油提供,蛋白質則來源於堅果,碳水化合物來自糖(極少量)和蜂蜜。
時光派點評
總的來説,週期性模擬禁食飲食確實是一款實用性、可實踐性更高的禁食方案。不過需要注意的是,目前的實驗結果還不能證實它能夠完全取代傳統的禁食方案,取得完全一致的有益效果,這也就需要科學家們繼續耕耘了。
在此之前,小編準備自己先試試PFMD,到時或許還有機會和大家分享我的體會呢。
聲明 - 本文內容僅用於科普知識分享與抗衰資訊傳遞,不構成對任何產品、技術或觀點的推薦、背書或功效證明。文內提及效果僅指成分特性,非疾病治療功能。涉及健康、醫療、科技應用等相關內容僅供參考,醫療相關請尋求專業醫療機構並遵醫囑,本文不做任何醫療建議。如欲轉載本文,請與本公眾號聯繫授權與轉載規範。
參考文獻
[1]Bloom, W., Fasting as an introduction to the treatment of obesity. Metabolism, 1959. 8: p. 214-220.
[2]Carlson, A.J. and F. Hoelzel, Apparent prolongation of the life span of rats by intermittent fasting: one figure. The Journal of nutrition, 1946. 31(3): p. 363-375.
[3]Manzanero, S., et al., Intermittent fasting attenuates increases in neurogenesis after ischemia and reperfusion and improves recovery. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 2014. 34(5): p. 897-905.
[4]Anson, R.M., et al., Intermittent fasting dissociates beneficial effects of dietary restriction on glucose metabolism and neuronal resistance to injury from calorie intake. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2003. 100(10): p. 6216-6220.
[5]Longo, V.D., et al., Replicative and chronological aging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell metabolism, 2012. 16(1): p. 18-31.
[6]Longo, V.D., et al., Human Bcl-2 reverses survival defects in yeast lacking superoxide dismutase and delays death of wild-type yeast. The Journal of cell biology, 1997. 137(7): p. 1581-1588.
[7]Kaeberlein, T.L., et al., Lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans by complete removal of food. Aging cell, 2006. 5(6): p. 487-494.
[8]Lee, G.D., et al., Dietary deprivation extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging cell, 2006. 5(6): p. 515-524.
[9]Fontana, L. and L. Partridge, Promoting health and longevity through diet: from model organisms to humans. Cell, 2015. 161(1): p. 106-118.
[10]Dong, T.A., et al., Intermittent fasting: a heart healthy dietary pattern? The American journal of medicine, 2020. 133(8): p. 901-907.
[11]Grajower, M.M. and B.D. Horne, Clinical management of intermittent fasting in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nutrients, 2019. 11(4): p. 873.
[12]Harris, L., et al., Intermittent fasting interventions for treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 2018. 16(2): p. 507-547.
[13]Volpe, S.L., Intermittent Fasting—What Is It and Does It Work? ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal, 2019. 23(1): p. 34-36.
[14]Wang, R., et al., Effects of the periodic fasting-mimicking diet on health, lifespan, and multiple diseases: a narrative review and clinical implications. Nutrition Reviews, 2024: p. nuae003.
[15]Brandhorst, S., et al., A periodic diet that mimics fasting promotes multi-system regeneration, enhanced cognitive performance, and healthspan. Cell metabolism, 2015. 22(1): p. 86-99.
[16]Flanagan, E.W., et al., Calorie restriction and aging in humans. Annual review of nutrition, 2020. 40: p. 105-133.
[17]Mirzaei, H., J.A. Suarez, and V.D. Longo, Protein and amino acid restriction, aging and disease: from yeast to humans. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2014. 25(11): p. 558-566.
[18]Becker, F., M.M. Behrends, and K.L. Rudolph, Evolution, mechanism and limits of dietary restriction induced health benefits & longevity. Redox Biology, 2023. 63: p. 102725.
[19]Caron, J.P., et al., Intermittent fasting: Potential utility in the treatment of chronic pain across the clinical spectrum. Nutrients, 2022. 14(12): p. 2536.
[20]Di Tano, M., et al., Synergistic effect of fasting-mimicking diet and vitamin C against KRAS mutated cancers. Nature Communications, 2020. 11(1): p. 2332.
[21]Longo, V.D. and M.P. Mattson, Fasting: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell metabolism, 2014. 19(2): p. 181-192.
[22]Longo, V.D. and S. Panda, Fasting, circadian rhythms, and time-restricted feeding in healthy lifespan. Cell metabolism, 2016. 23(6): p. 1048-1059.
[23]Goldberg, E.L., et al., Lifespan‐extending caloric restriction or m TOR inhibition impair adaptive immunity of old mice by distinct mechanisms. Aging cell, 2015. 14(1): p. 130-138.
[24]Barnosky, A.R., et al., Intermittent fasting vs daily calorie restriction for type 2 diabetes prevention: a review of human findings. Translational Research, 2014. 164(4): p. 302-311.
[25]Bartke, A. and J. Darcy, GH and ageing: Pitfalls and new insights. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2017. 31(1): p. 113-125.
[26]Mishra, A., et al., Fasting-mimicking diet prevents high-fat diet effect on cardiometabolic risk and lifespan. Nature metabolism, 2021. 3(10): p. 1342-1356.
[27]Wei, M., et al., Fasting-mimicking diet and markers/risk factors for aging, diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. Science translational medicine, 2017. 9(377): p. eaai8700.
[28]Videja, M., et al., Fasting-mimicking diet reduces trimethylamine N-oxide levels and improves serum biochemical parameters in healthy volunteers. Nutrients, 2022. 14(5): p. 1093.
[29]Maloh, J., et al., The Effects of a Fasting Mimicking Diet on Skin Hydration, Skin Texture, and Skin Assessment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2023. 12(5): p. 1710.
[30]Longo, V.D. and R.M. Anderson, Nutrition, longevity and disease: From molecular mechanisms to interventions. Cell, 2022. 185(9): p. 1455-1470.
[31]Zhou, Z.-L., et al., Neuroprotection of fasting mimicking diet on MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mice via gut microbiota and metabolites. Neurotherapeutics, 2019. 16: p. 741-760.
[32]Rangan, P., et al., Fasting-mimicking diet cycles reduce neuroinflammation to attenuate cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s models. Cell reports, 2022. 40(13).
[33]Zhao, J., et al., Improvement of Non‐Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice by Intermittent Use of a Fasting‐Mimicking Diet. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2021. 65(23): p. 2100381.
[34]Zhao, N., et al., Glycemic control by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes effects of fasting-mimicking diet on type 2 diabetic mice. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2021. 12(1): p. 1-14.
[35]Salvadori, G., et al., Fasting-mimicking diet blocks triple-negative breast cancer and cancer stem cell escape. Cell metabolism, 2021. 33(11): p. 2247-2259. e6.